Fusion & Fission
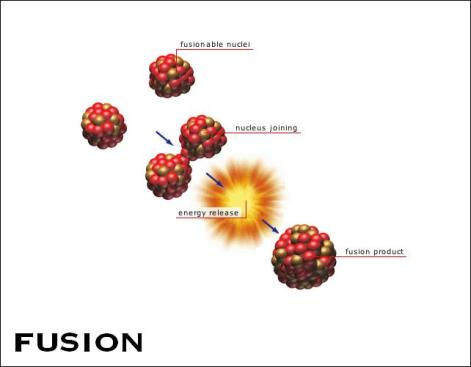
Nuclear fusion is when two or more nuclei with small masses fuse together, hence fusion, by smashing into each other. They form a larger nucleus and release large amounts of energy. The downside of nuclear fusion is that it requires temperatures of over 100,000,000 degrees Celsius. Nuclear fusion is occurring constantly in the sun, which causes it to shine. If you look at it one way, nuclear fusion is what sustains life on earth by providing heat and light. However, nuclear fusion reactors called International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactors (ITER) are in the works. The plus side of nuclear fusion is that its safer, cleaner, more efficient and produces more energy that nuclear fission which is what nuclear power plants use today.
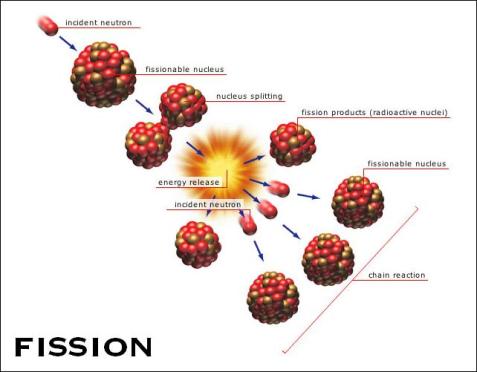
Nuclear fission is the division of a large nucleus, it splits into smaller nuclei and releases energy. Nuclear fission is what nuclear power plants use today and it provides 17% of the world’s electricity. The most common atom used in the fission process is uranium. The uranium atom is split apart by a neutron, which sends more neutrons to other uranium atoms causing them to divide, and so on and so forth. This is called a chain reaction. If the chain reaction is not controlled, then there will be a huge explosion. However, in nuclear power plants, the chain reaction is regulated so it does not go too fast and become disastrous.
Intramolecular force is any force that holds together the atoms making up a molecule or a compound. There are three main types of intramolecular force, ionic, covalent, and metallic. These forces create attractions between atoms and strengthen bonds in molecules and compounds. The attraction of the atoms changes the compound, creating new and different partners. In nuclear reactions, splitting apart nuclei and fusing them together changes the area around the nuclei, because energy is leaving them so fast.
Leave a comment